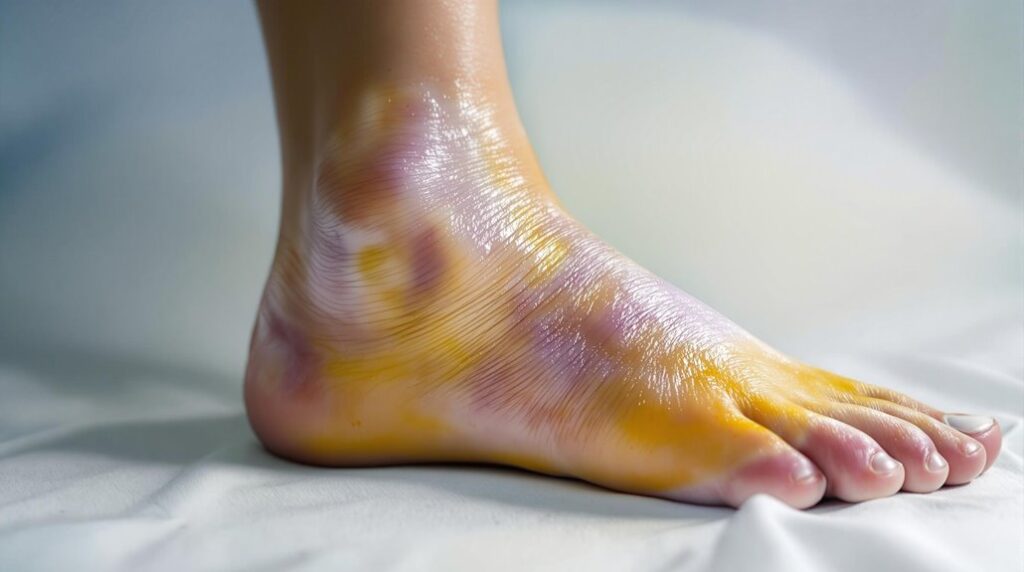
Ligament damage in your foot, commonly called a sprain, occurs when the fibrous tissues connecting your bones stretch or tear. Symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness, and possibly bruising. Common causes range from sudden movements during sports to improper footwear. Initial treatment follows the PRICE method: protect, rest, ice, compress, and elevate the injured area. Rehabilitation is essential for recovery, focusing on strength and balance. Understanding the nature and implications of ligament injuries can guide effective management strategies going forward.
Understanding Ligament Damage
When you experience ligament damage in your foot, it's important to understand what this injury entails and how it affects your overall mobility. Ligament damage, often called a sprain, occurs when the fibrous tissues connecting bones at a joint become stretched or torn. The severity of the injury is classified into three grades: Grade I is mild, Grade II is moderate, and Grade III indicates a complete tear. Such injuries often result from sudden movements like twisting or awkward landings. Treatment typically follows the PRICE method—Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Depending on the severity, you may also need physical therapy or, in extreme cases, surgical intervention. Understanding these aspects can help you manage recovery effectively.
Symptoms of a Foot Sprain
Ligament damage in the foot, commonly referred to as a sprain, presents a range of symptoms that can greatly impact your daily activities. You might experience pain, tenderness, and swelling around the affected area, particularly in the ankle or foot ligaments. Bruising could also appear, indicating damage to nearby blood vessels. As a result of this injury, you may find it difficult to bear weight on the injured foot, considerably reducing your mobility. Additionally, muscle spasms or cramping may occur, reflecting painful tightening in response to the sprain. The severity of these symptoms can vary, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and functional impairment, making it essential to assess your condition promptly and seek appropriate care.
Causes of Ligament Injury
Injuries to the ligaments in your foot can occur due to a variety of factors, with sudden movements often playing a critical role. Activities like basketball or soccer frequently involve quick twists, turns, or impacts that can lead to ligament damage. Additionally, overstretching during physical activities, especially when you skip proper warm-ups, heightens this risk. High-impact exercises on uneven surfaces can cause unexpected ankle rolls or sprains, further contributing to injuries. If you've had previous foot injuries or possess weak ankle ligaments, your chances of re-injury increase considerably. Furthermore, wearing inappropriate footwear without adequate support during intense activities can exacerbate the situation, making you more susceptible to ligament injuries in your foot.
Immediate Steps to Take After Injury
After experiencing a foot injury, it is vital to act swiftly to minimize damage and promote recovery. First, protect the injured area by avoiding any weight on it. Look for signs of ligament damage, such as pain, swelling, or bruising. If you notice significant swelling, apply ice for 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours. Compress the foot gently with a bandage, but make sure it's not too tight to avoid cutting off circulation. Elevate your foot to help reduce swelling. Avoid heat, alcohol, and massages during the initial days, as these can worsen swelling. If you experience severe pain, significant swelling, or if symptoms persist, seek urgent medical advice. Immediate attention is imperative, especially if a cracking sound occurred during the injury.
The PRICE Method for Treatment
When dealing with a foot injury, applying the PRICE method can greatly aid in your recovery process. This approach, which stands for Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation, is vital for the first 2 to 3 days post-injury. Begin by protecting the injured area with supportive footwear or braces to prevent further damage. Resting the foot is imperative; avoid putting weight on it to facilitate healing. Apply ice to the injury for up to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours to minimize swelling and pain. Use elastic bandages for compression, as they help control swelling. Finally, elevate your foot above heart level to reduce fluid accumulation, promoting a more effective recovery process.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing the right moment to seek medical attention can greatly impact the outcome of your foot injury. If you're experiencing severe pain that worsens over time, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional to rule out ligament damage. Significant swelling or bruising that continues to increase may indicate a more serious injury requiring evaluation. Difficulty putting weight on your foot or an inability to move it normally suggests potential ligament damage, which warrants immediate medical assessment. Hearing a crack at the time of injury or noticing a change in the shape of your foot necessitates urgent care. Additionally, symptoms like numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles sensation could signal nerve involvement, demanding prompt medical attention.
Preventing Future Injuries
To effectively prevent future ligament injuries in your foot, it's crucial to adopt a thorough approach that includes proper warm-up routines, strength training, and appropriate footwear. Always begin your physical activities with a warm-up to increase blood flow to your muscles and minimize the risk of injury. Incorporating strengthening exercises for the ankles and feet can greatly reduce the likelihood of ligament damage. Choosing footwear that offers proper support and cushioning is important during sports or physical activities, as it alleviates stress on ligaments. Additionally, integrating flexibility and balance training into your routine enhances stability, further lowering the chance of sprains. Finally, be mindful of your body's limits, gradually increasing workout intensity to prevent overstretching and potential ligament damage.
Rehabilitation and Recovery Tips
Effective rehabilitation and recovery from ligament damage in your foot involves a systematic approach that prioritizes gradual progression and tailored exercises. Start with gentle range-of-motion exercises as soon as pain permits, then advance to strength training to rebuild functionality. Incorporate proprioceptive training, like balance exercises on unstable surfaces, to enhance coordination and stability. It's essential to use a graduated return-to-activity method, beginning with low-impact exercises before shifting to higher-impact activities, reducing the risk of re-injury. Consider physical therapy for personalized rehabilitation programs, which may include ultrasound or electrical stimulation to support healing. Finally, maintain a consistent routine of stretching and strengthening exercises to guarantee flexibility and prevent future ligament injuries, keeping your foot healthy and functional.